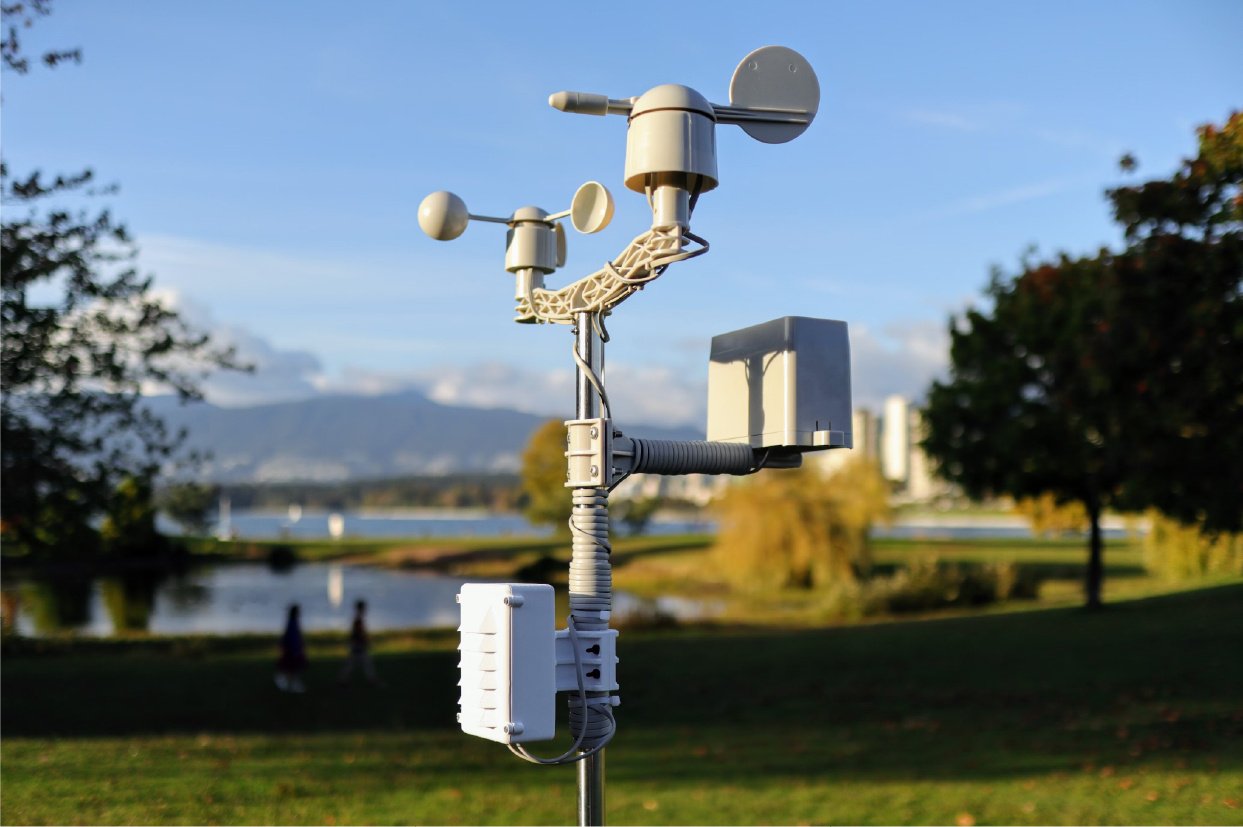
Many large cities around the world such as Copenhagen, Bangkok, Paris, New York, Shanghai, Seoul, and many others have already implemented ambitious Smart City initiatives, and their success has inspired other cities around the world to follow in their footsteps. As we will see, the integration of IoT is vital to the success of these projects – providing real-time data to better support quality-of-life improvements.
IoT technology in service of smart city initiatives includes monitoring units, cameras, sensors, and other mechanised devices. By collecting pertinent data and routing it toward an AI-powered central database, IoT systems push the smart city concept closer to its full potential. Below are some real-world examples of how IoT is already impacting smart city communities.

Utilities
Utility companies can take advantage of real-time data to optimise the provision of electricity or water to a particular area in the city, or to automatically control smart signs and street-lights.
For instance, if a certain area routinely requires more resources at particular times of the day or week, or if early signs of a demand spike are detected by networked sensors, utility providers can divert resources to that area, resulting in a lower likelihood of service interruption. Smart metering can help pre-empt related demand issues, maximising efficiency in the long run – and passing the resulting cost savings down to consumers.
Some cities are using the power of IoT to develop additional benefits as well. Copenhagen, for instance, collects and processes weather data in real time, using it to automatically regulate temperatures inside buildings. The same approach can be applied in tropical regions such as Thailand where it is hot and the humidity makes it even worse. Should there be a drop in temperature, the smart building approach will work well in cooling rooms as air conditioning units do not have to work as hard, meaning less pressure and extremely energy saving!

Traffic control
Smart cities can also benefit from traffic monitoring devices powered by IoT technology. In order to tackle pollution, cameras and sensors can help regulate the timing of traffic lights for greater efficiency in fuel costs and emissions, whilst also reducing congestion too.
Moreover, connectivity across public transport systems can improve people’s travelling experience and reduce the need to own a personal vehicle. People can use their mobile devices to check live public transport schedules, potentially saving travel time as well as fuel. For those who continue to drive cars, cities such as London have already implemented smart parking technology to reduce congestion, by providing drivers with data on available parking spaces.
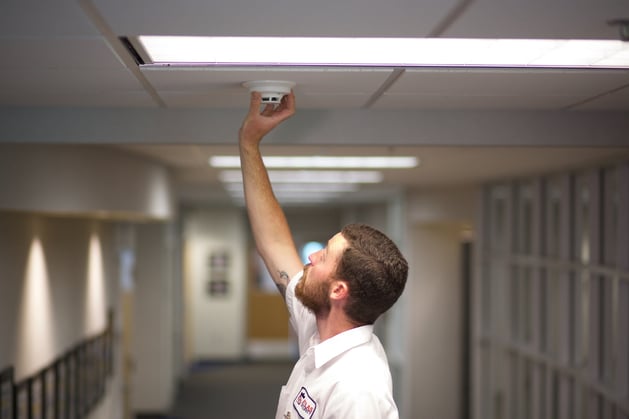

Public safety
Throughout an IoT-connected smart city, CCTV cameras, smoke detectors, and water level monitoring systems have the potential to greatly improve public safety, for example diseases such as legionnaires can also be detected via smart sensors in water pipes which maintains water quality. If a crime was committed or fire breaks out in a certain area of the city, sensors will alert all nearby city officials and emergency response teams, greatly improving response time. The same systems can automatically divert traffic as well, allowing first responders to arrive at the location sooner.
IoT can also play a role in improving government response to both natural disasters and infrastructure failures. Cities prone to flooding can use sensors to detect rising water levels – either from rainfall or improper waste management. These sensors can automatically trigger the operation of flood gates, and alert waste management authorities of blockages that are affecting the sewage system.

Environment
Monitoring the weather, air and water quality, and waste systems through IoT networks can greatly benefit both residential and commercial neighbourhoods. For instance, sensors that detect air quality can provide live data feeds through people’s smartphones, and transmit data to electronic billboards around the city to indicate whether it’s safe to travel outside.
IoT water quality monitoring systems can alert city officials to potential contamination of the city’s water supply. Waste management authorities can be alerted when a particular trash/recycle container is full. Timely waste collection can prevent overflows that might otherwise pollute the surrounding environment or cause blockages, hazardous waste contamination, and foul smells.

Finding the right applications
Given the diverse uses of IoT paired with smart city technology, different cities may need to emphasise different applications first. Ultimately the priorities of each city government will depend on local conditions, and officials may begin by investing their smart city / IoT resources to control traffic, air pollution, or some other issue.
This level of versatility highlights the remarkable value of IoT and smart city initiatives. Through careful design and implementation, these tech-based enhancements can bring wonders to the livelihood of the local populace, letting everyone benefit from the increased efficiency, public well-being, and cost-saving measures they introduce.
Summary
Many large cities around the world such as Copenhagen, Bangkok, Paris, New York, Shanghai, Seoul, and many others have already implemented ambitious Smart City initiatives, and their success has inspired other cities around the world to follow in their footsteps. As we will see, the integration of IoT is vital to the success of these projects – providing real-time data to better support quality-of-life improvements.